
Table of Contents
ToggleMany businesses try random edits when rankings drop. They change categories, rewrite descriptions, or add services without a clear reason. Guessing like this wastes time and often creates instability.
When you reverse engineer Google Business Profile listings that consistently rank, you stop guessing and start observing patterns. Map pack rankings do not happen by accident. Google rewards profiles that show consistent signals in categories, reviews, activity, and geographic relevance.
Top-performing listings usually share:
These patterns repeat across competitive markets.
Reverse engineering does not mean copying or looking for shortcuts. It reveals structure. You identify what Google consistently rewards and apply those insights safely to your own profile.
Instead of testing random changes, you base improvements on real competitive evidence and proven competitor optimization methods. This approach protects stability, reduces risk, and supports long-term map pack growth.
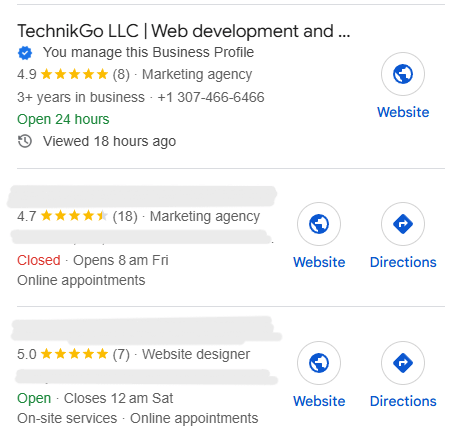
High-performing listings rarely rank by accident. When you compare top map pack results across different cities and industries, clear structural similarities appear. These patterns help explain why certain profiles maintain consistent visibility.
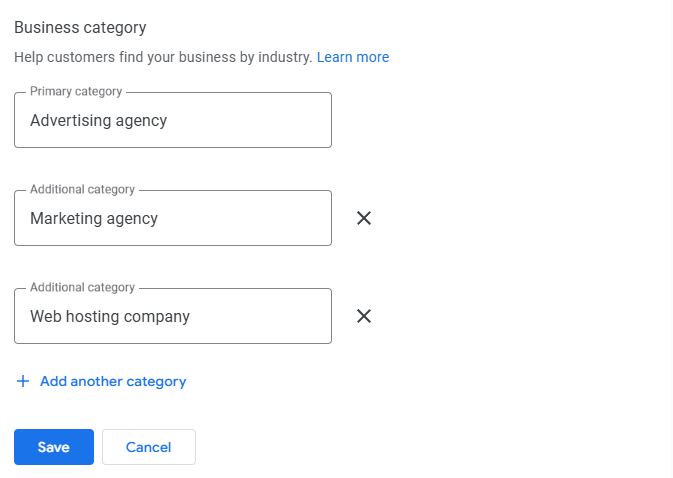
Category selection forms the foundation of local relevance. High-performing listings show strong alignment and stability.
Beyond categories, clarity strengthens ranking performance.
When these elements work together, Google sees strong relevance and consistency – two key signals behind sustained map pack visibility.
Competitor optimization often appears subtle, but strong patterns exist when you look closely. Top-ranking profiles do not rely on one factor. They maintain consistent activity across multiple signals that Google evaluates together.
High-ranking competitors usually receive reviews at a steady pace. They do not depend on large spikes followed by long silence. Consistent review growth signals ongoing customer engagement and business activity.
Look for:
Competitor optimization often includes steady photo updates. High-performing listings add fresh images over time, not all at once.
Patterns to observe:
Top competitors post updates with clear intent. They highlight services, updates, or announcements regularly. Posting supports profile freshness and reinforces relevance.
The key is consistency, not volume.
High-performing listings rarely leave sections empty. They complete services, attributes, business descriptions, and operational details. Complete profiles send stronger relevance and trust signals.
When these competitor optimization signals align, Google receives multiple confirmation points. Visibility becomes consistent because the profile shows stability, activity, and clear intent.
To reverse engineer Google Business Profile rankings effectively, you must follow a structured comparison process. This method reveals repeatable patterns instead of random differences.
Start by searching your main service keywords across different locations in your target area. Identify businesses that appear repeatedly in the map pack.
Focus only on competitors who:
These are the listings worth analyzing.
Check the primary category of each top competitor. Look for overlap. If most high-ranking listings share the same primary category, that category likely matches Google’s intent mapping for the keyword.
Avoid copying blindly. Look for alignment patterns.
Study how often competitors receive reviews and how they respond. Note:
Steady review velocity often supports ranking stability.
Compare listed services, attributes, and profile details. High-ranking listings usually show clear service focus and matching intent signals across categories and descriptions.
Look for clarity, not volume.
Use grid-based tracking to see where competitors dominate. Identify zones where they consistently rank and where visibility drops.
Geographic patterns reveal whether rankings depend on proximity or structured optimization.
Following these steps helps you reverse engineer Google Business Profile performance safely and apply insights without creating instability.
GMB competitive insights help you understand why certain listings rank – but you must separate legal optimization from guideline violations. Not every visible tactic is safe to copy.
Start by identifying repeatable patterns across multiple high-ranking listings. If several competitors share the same category structure, review consistency, and profile completeness, those patterns likely reflect legitimate optimization.
However, if only one listing ranks due to obvious keyword stuffing or suspicious tactics, that is a violation – not a strategy.
Some competitors add services, cities, or marketing phrases to their business name. This may temporarily boost relevance, but it increases suspension risk.
Do not copy:
Short-term gains often lead to long-term penalties.
Extract GMB competitive insights that improve structure safely, such as:
Structural improvements build trust and long-term visibility. Reverse engineering should strengthen your profile – not expose it to unnecessary risk.
Map pack visibility changes based on location. To reverse engineer rankings properly, you must understand how proximity and geographic strength affect performance.
Google prioritizes businesses closer to the searcher. A listing may rank #1 near its address but drop significantly a few miles away.
When analyzing competitors, ask:
This helps you separate proximity advantage from optimization strength.
Geo-grid tracking reveals ranking patterns across multiple points in a service area. Instead of one position number, you see a heatmap of visibility.
These insights show:
Grid-based analysis provides a realistic picture of map pack coverage.
High-performing competitors often dominate specific neighborhoods or service corridors. These dominance zones indicate strong relevance and trust signals in those areas.
Identifying these zones helps you:
Location-based analysis turns reverse engineering into a structured, data-driven process instead of random adjustments.
Reverse engineering only creates value when you apply insights correctly. The goal is not to copy competitors – it is to understand what works and improve your profile in a structured way.
When you analyze top-performing listings, you uncover:
These insights guide specific improvements instead of random edits.
Structured optimization focuses on stability and consistency. Instead of changing multiple elements at once, you adjust one area based on clear competitive evidence. This reduces volatility and protects ranking trust.
Safe implementation matters. Large, sudden profile changes often trigger filters or instability. A professional Google Business Profile optimization service helps translate reverse engineering insights into controlled, compliant updates that support long-term map pack growth.
Reverse engineering works only when done carefully. Many businesses damage their own rankings by applying insights the wrong way. Avoid these common mistakes.
Reverse engineering should strengthen structure, not create volatility. Controlled, data-based adjustments protect long-term map pack performance.
Reverse engineering often uncovers gaps that directly explain ranking differences. These gaps are not random – they show where your profile lacks alignment compared to high-performing competitors.
If top competitors share the same primary category and yours differs, Google may see your listing as less relevant for key searches. Even small category misalignment can reduce map pack visibility.
Review both primary and secondary categories to ensure they match real search intent.
Consistent review growth supports prominence. If competitors receive steady monthly reviews while your profile shows long gaps, ranking stability may suffer.
Review velocity signals ongoing activity and trust.
Grid tracking often reveals limited visibility outside your immediate location. If competitors rank across multiple neighborhoods and you do not, geographic strength may be uneven.
This gap often connects to proximity influence and optimization differences.
High-performing profiles clearly define their services. If your listing lacks detailed service entries or relevant attributes, Google receives weaker relevance signals.
Identifying these gaps helps prioritize structured improvements instead of guessing which changes to make first.
Use this checklist to ensure your reverse engineering process stays strategic, accurate, and compliant.
Following this checklist helps you reverse engineer Google Business Profile listings safely and apply insights without creating ranking instability.
Reverse engineering works best when you focus on analysis, not imitation. The goal is to understand why certain listings rank – not to copy visible elements without context.
Structured, data-based changes create stable growth. When you rely on competitive patterns, category alignment, review trends, and geographic data, your improvements become intentional instead of reactive.
Reverse engineering is not a one-time task. Local competition evolves, categories shift, and review patterns change. Ongoing analysis keeps your Google Business Profile aligned with market conditions and protects long-term map pack visibility.